August 15, 2024

From the 2024 UPC Illustrated Training Manual, Chapter 12 – FUEL GAS PIPING
1208.10.1 Overpressure Protection Required. Where piping systems serving appliances designed to operate with a gas supply pressure greater than 14 inches water column (3.5 kPa) are required to be equipped with overpressure protection by Section 1208.8, each overpressure protection device shall be adjusted to limit the gas pressure to each connected appliance as required by the appliance manufacturer’s installation instructions. [NFPA 54:5.8.2.2]
1208.10.2 Overpressure Protection Devices. Each overpressure protection device installed to meet the requirements of this section shall be capable of limiting the pressure to its connected appliance(s) as required by this section independently of any other pressure control equipment in the piping system. [NFPA 54:5.8.2.3]
When choosing overpressure protection systems, in general there are three things to consider:
- Continuity of service – does the user, or the load, need to be continuously supplied with gas?
- Containment – is gas released into the atmosphere or does it remain contained within the gas system?
- Alerting – is there provision for notification or warning that an emergency has occurred, and that the overpressure protection equipment has gone into operation? See Figure 1208.8.
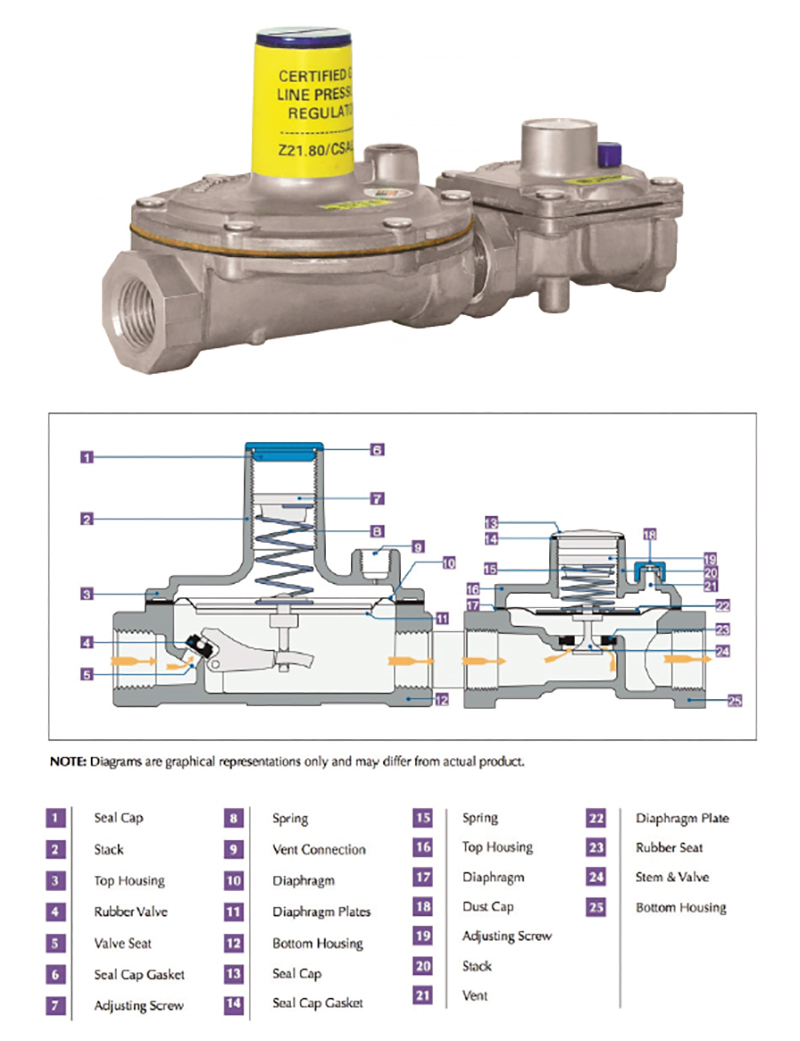
(Courtesy of Maxitrol Company)
From the 2024 UMC Illustrated Training Manual, Chapter 3 – GENERAL REGULATIONS
303.4 Anchorage of Appliances. Appliances designed to be fixed in position shall be securely fastened in place in accordance with the manufacturer’s installation instructions. Supports for appliances shall be designed and constructed to sustain vertical and horizontal loads within the stress limitations specified in the building code.
Usually, the method of securing an appliance in place, if required, is provided in the manufacturer’s installation instructions as one of the conditions of listing. Generally speaking, equipment regulated by the code should be securely fastened in place except for residential washers, dryers, kitchen ranges and equipment defined as Portable by Section 218.0. In Seismic Zones C, D, E and F (see the building code for definitions and location of these active seismic zones), it is suggested that a competent engineer evaluate the methods of securing the equipment in the event the manufacturer’s instructions do not include guidance.
A major reason for requiring equipment to be secured in place is to prevent damage to electrical, gas or refrigerant piping connections due to vibration or shifting of equipment during a seismic event. Figure 303.4 illustrates various methods of anchoring appliances.
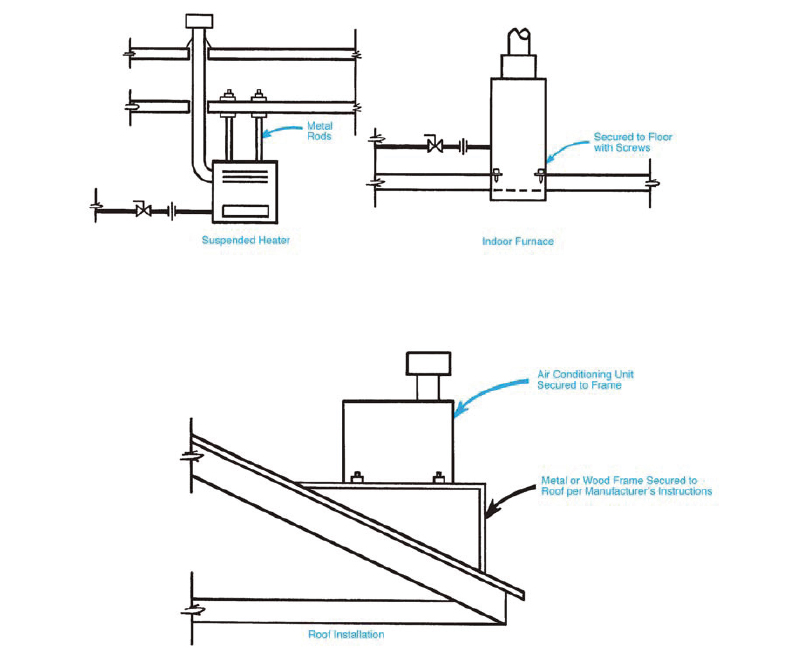
(This is not to be considered the official position of IAPMO, nor is it an official interpretation of the Codes.)

IAPMO
IAPMO develops and publishes the Uniform Plumbing Code®,the most widely recognized code of practice used by the plumbing industry worldwide; Uniform Mechanical Code®; Uniform Swimming Pool, Spa and Hot Tub Code®; and Uniform Solar Energy, Hydronics and Geothermal Code™ — the only plumbing, mechanical, solar energy and swimming pool codes designated by ANSI as American National Standards — and the Water Efficiency Standard (WE-Stand)™. IAPMO works with government, contractors, labor force, and manufacturers to produce product standards, technical manuals, personnel certification/educational programs and additional resources in order to meet the ever-evolving demands of the industry in protecting public health and safety.
Last modified: October 10, 2024
