
From the 2024 UPC Illustrated Training Manual, Chapter Chapter 7, SANITARY DRAINAGE
702.2 Intermittent Flow. Drainage fixture units for intermittent flow into the drainage system shall be computed on the rated discharge capacity in gallons per minute (gpm) (L/s) in accordance with Table 702.2.
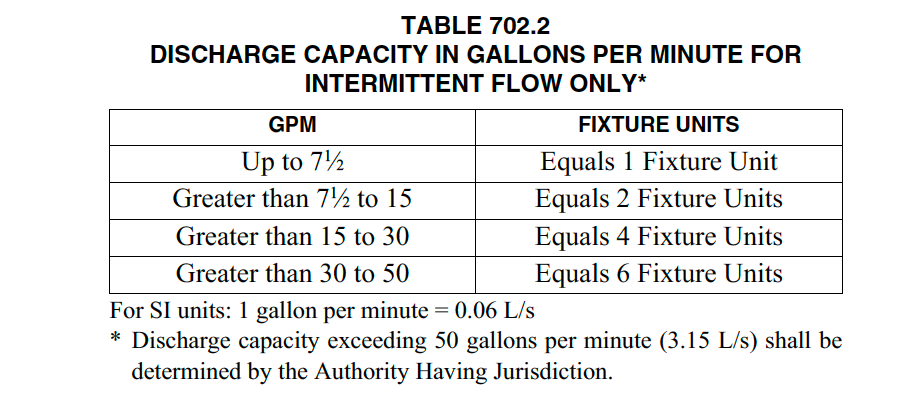
Intermittent flows differ from continuous flows. Intermittent flows derive from fixtures discharging into the drainage system that are subject to the predictability of being on or off during a period of time. All the fixtures in Table 702.1 have intermittent flows and therefore are assigned fixture units as discussed in the commentary for Section 702.1. With respect to fixture discharge, each fixture unit is equivalent to 7.5 gallons per minute (GPM). Table 702.2 shows discharge capacities in gallons per minute computed to fixture units up to 50 gpm. This table could be used for fixtures or appliances not listed in Table 702.1 that have a known discharge rate. For example, there are many types and sizes of commercial dishwashers, glassware washers, pots and pans washers, etc. that are not listed in Table 702.1. Fixture unit values may be determined from the discharge rate (gpm) of the appliance. Notice that Table 702.2 states “For Intermittent Flow Only.”
Discharges from pumps are not applicable to this table because the flow is not derived from fixtures or appliances discharging immediately into the drainage system. The discharges are first collected into a sump and when reaching the sump’s capacity, a pump produces a continuous discharge flow into the drainage system. There is no element of predictability when the pump will be on or off during a period of time. Also, the rates of discharge of most pumps exceed Table 702.2. These discharges are called continuous and fall under the requirements of Section 702.3. The fixture unit values in Table 702.1 are applied in Table 703.2 by taking into account intermittent use and the probability of the fixture being on or off. For flows over 50 gpm, the Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) will determine the fixture unit value of the fixture.
From the 2024 UMC Illustrated Training Manual, Chapter Chapter 6, DUCT SYSTEMS
602.6 Vibration Isolators. Vibration isolation connectors installed between mechanical equipment and metal ducts (or casings) shall be made of an approved material and shall not exceed 10 inches (254 mm) in length.
Vibration isolators (flexible connections) minimize noise and vibration from mechanical equipment. Without them, excessive operating noise and premature weakening of joints and supports could result. Vibration isolators shall be made of approved materials. Neoprene and rubber are the common materials for this purpose, and good installation practices would provide adequate supports on both sides of these isolators. Figure 602.6 illustrates typical isolator details and points of installation within a system.
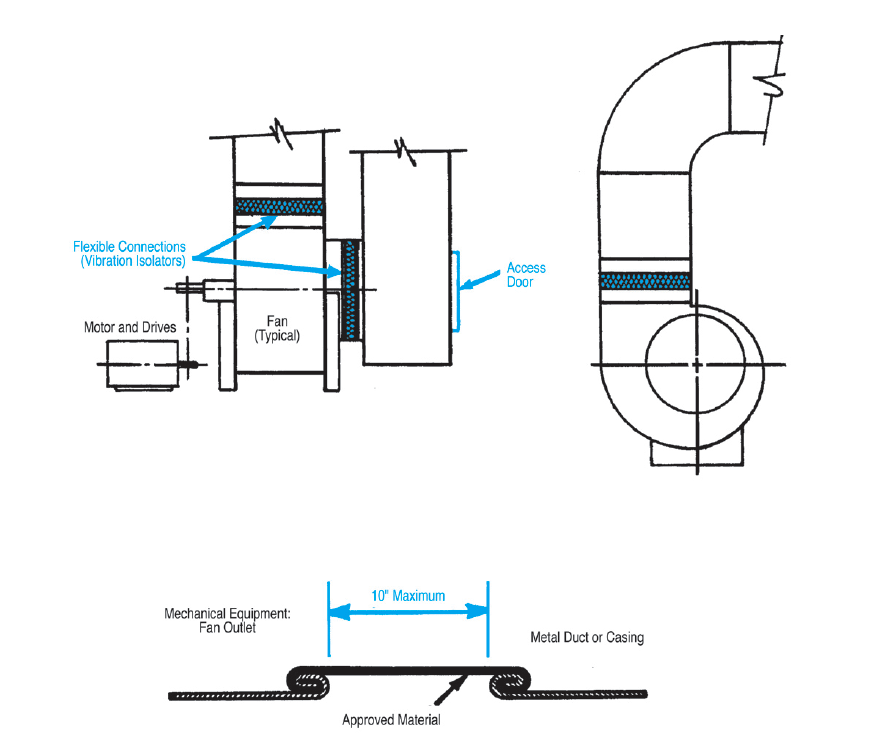
VIBRATION ISOLATOR DETAILS
(This is not to be considered the official position of IAPMO, nor is it an official interpretation of the Codes.)

IAPMO
IAPMO develops and publishes the Uniform Plumbing Code®,the most widely recognized code of practice used by the plumbing industry worldwide; Uniform Mechanical Code®; Uniform Swimming Pool, Spa and Hot Tub Code®; and Uniform Solar Energy, Hydronics and Geothermal Code™ — the only plumbing, mechanical, solar energy and swimming pool codes designated by ANSI as American National Standards — and the Water Efficiency Standard (WE-Stand)™. IAPMO works with government, contractors, labor force, and manufacturers to produce product standards, technical manuals, personnel certification/educational programs and additional resources in order to meet the ever-evolving demands of the industry in protecting public health and safety.
Last modified: May 23, 2024
