December 5, 2024

From the 2024 UPC Illustrated Training Manual, Chapter 11 – STORM DRAINAGE
1101.12.2.2 Secondary Roof Drain. Secondary roof drains shall be provided. The secondary roof drains shall be located not less than 2 inches (51 mm) above the roof surface. The maximum height of the roof drains shall be a height to prevent the depth of ponding water from exceeding that for which the roof was designed as determined by Section 1101.12.1. The secondary roof drains shall connect to a piping system in accordance with Section 1101.12.2.2.1 or Section 1101.12.2.2.2.
If roof drains are provided for the secondary system, they must be located so that they will be a minimum of 2 inches higher than the inlet of the primary roof drain (see Figures 1101.12.2 and 1101.12.2.2). The drain must also be placed so that it will serve the area of the primary drain. Care must also be taken that the ponding of water, which will occur if the primary drain does not drain, does not exceed the structural capacity of the roof. The roof must be designed with the weight of that standing water in mind.
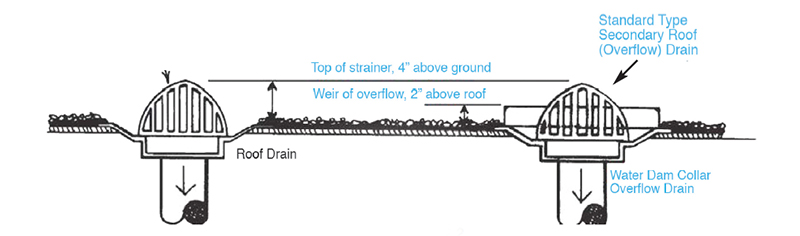
PRIMARY AND SECONDARY ROOF DRAINS – SECONDARY DRAIN WEIR 2 INCH ABOVE PRIMARY – STRAINER 4 INCH ABOVE THE ROOF

PRIMARY AND SECONDARY ROOF DRAINS – SECONDARY WITH 2 INCH WEIR
From the 2024 UMC Illustrated Training Manual, Chapter 10 – BOILERS AND PRESSURE VESSELS
1001.5 Mounting. Equipment shall be set or mounted on a level base capable of supporting and distributing the weight contained thereon. Boilers, tanks, and equipment shall be securely anchored to the structure. Equipment requiring vibration isolation shall be installed as designed by a registered design professional and approved by the Authority Having Jurisdiction.
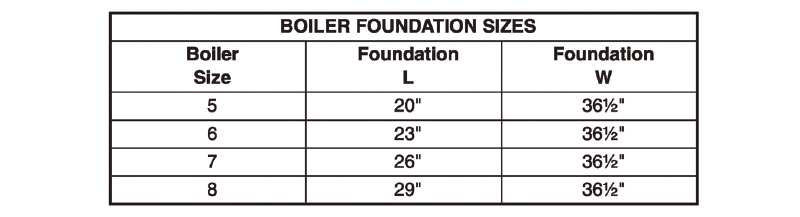
Manufacturers are clear in the installation instructions about boiler foundation requirements. Here’s an example:
Boiler Foundation
Never install boiler on combustible flooring or carpeting, even if a concrete or aerated foundation is used. Severe personal injury, death or substantial property damage can result.
- A level concrete or solid brick pad is required if:
a) There is a possibility of the floor becoming flooded.
b) Non-level conditions exist. - An aerated boiler foundation is recommended if any of the following conditions exist:
a) Electrical wiring or telephone cables buried in the concrete floor of the boiler room.
b) Concrete floor is “green.”
c) There is a history of the floor becoming flooded.
d) Water is channeled under the concrete.
This manufacturer varies the length and width dimensions based on the model of boiler. In Figure 1001.5a, the manufacturer felt 2-inch-thick concrete was sufficient to support the weight.
Vibration isolation devices provide deterrence to “telegraphed” boiler noises to the surrounding hard surfaces. In addition, boilers, pumps, and piping should be included in any vibration isolation strategy (see Figure 1001.5b).
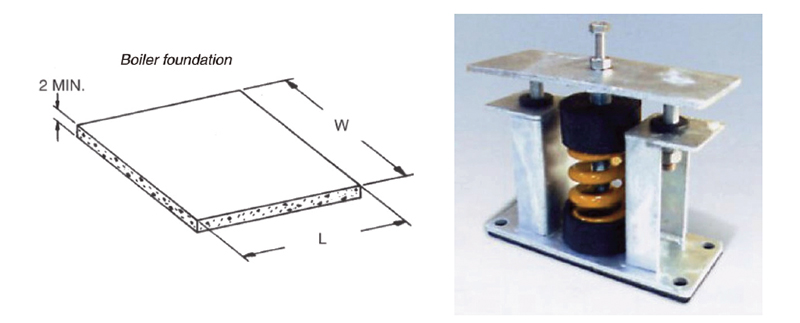
Right: FIGURE 1001.5B: SPRING MOUNT – EXAMPLE OF VIBRATION ISOLATION STRATEGY
(This is not to be considered the official position of IAPMO, nor is it an official interpretation of the Codes.)

IAPMO
IAPMO develops and publishes the Uniform Plumbing Code®,the most widely recognized code of practice used by the plumbing industry worldwide; Uniform Mechanical Code®; Uniform Swimming Pool, Spa and Hot Tub Code®; and Uniform Solar Energy, Hydronics and Geothermal Code™ — the only plumbing, mechanical, solar energy and swimming pool codes designated by ANSI as American National Standards — and the Water Efficiency Standard (WE-Stand)™. IAPMO works with government, contractors, labor force, and manufacturers to produce product standards, technical manuals, personnel certification/educational programs and additional resources in order to meet the ever-evolving demands of the industry in protecting public health and safety.
Last modified: December 5, 2024
